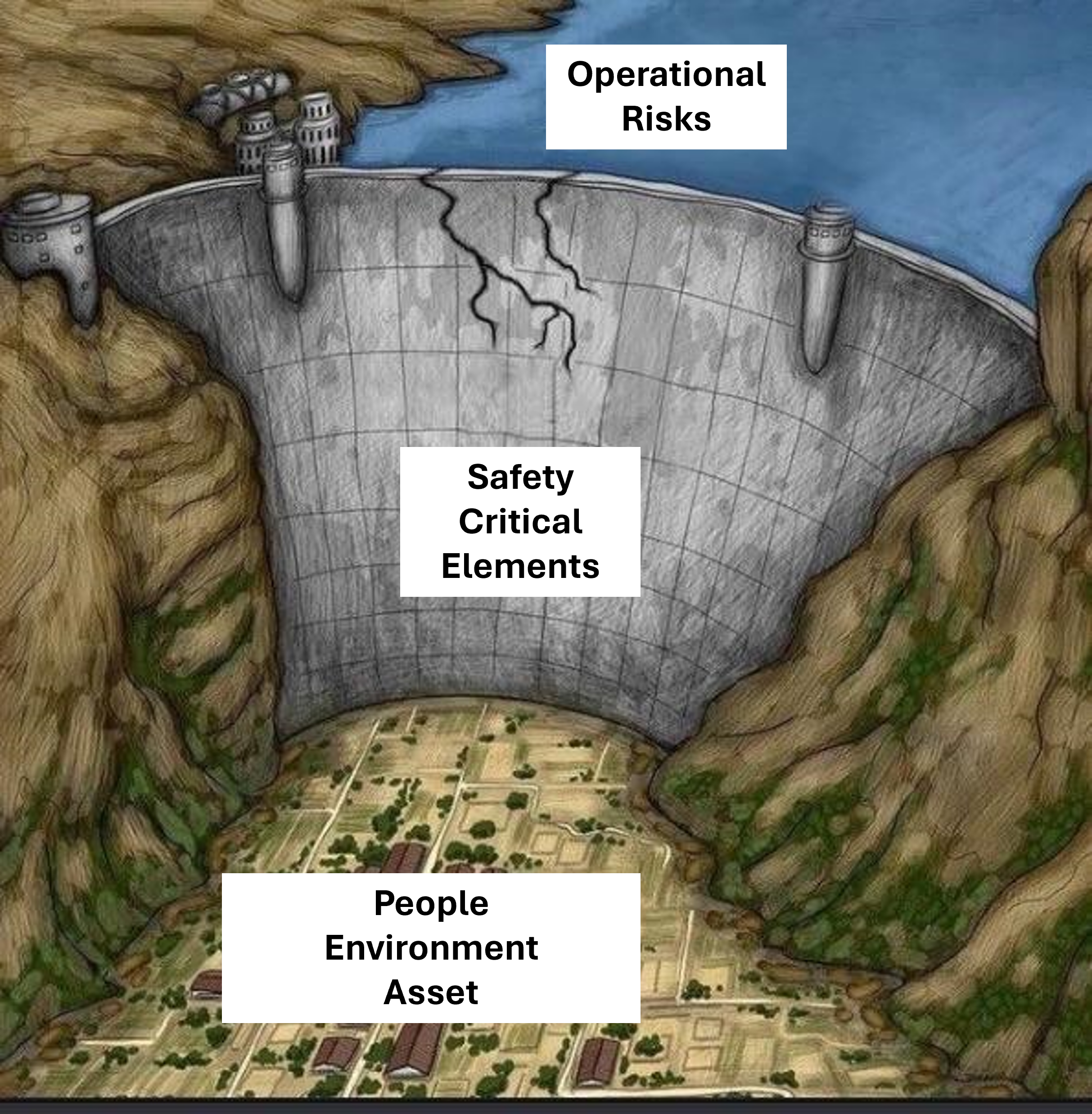
Proactive Risk Mitigation: Safety Critical Elements
In high-hazard industries such as oil and gas or petrochemicals, safety is a complex landscape. Hazards can be difficult to understand and even more challenging to protect against. Understanding what is keeping your operations safe and ensuring the integrity and reliability of those Safety Critical Elements (SCE) is essential for protecting personnel, the environment, and assets from potential harm. These are any elements of an installation that could fail and cause or contribute to an incident or are designed or intended to mitigate operational risk.
Failure to keep your safety critical elements functional is one of the many reasons organization have either fire, explosion, and/or release of toxic chemicals or gases. The Center for Chemical Process Safety (CCPS) published a summary of the events of an alumina slurry digestion/flash system which caused a vessel rupture in a Boling Liquid Vapor Explosion (BLEVE) that caused permanent injuries to 29 people in the February 2019 issues of the Beacon newsletter (link here). This incident is a reminder of the importance of knowing the functionality of your SCE, their availability, reliability, survivability, and interactions/dependencies.
Where do Safety Critical Elements come from?
Identifying safety critical elements starts at the earliest stages of a facility's lifecycle. In engineering feasibility studies, there are activities undertaken to conduct risk assessments, select building materials, and develop high-level designs that include elements that will be found on a future safety critical elements list. As the design progresses through FEED and detailed engineering that list is modified, some of these elements will be removed, others modified, and new ones added through various risk assessments and design activities along the way. Once the facility is constructed and operational, that’s when the focus shifts to optimization and maintenance.
Basic Categories of Safety-Critical Elements:
Mechanical Equipment: Mechanical equipment forms the backbone of operations in industrial facilities, ranging from pumps and valves to pressure vessels and pipelines. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential to prevent equipment failures, leaks, and other potential hazards.
Instruments: Instrumentation and control systems are vital for monitoring and regulating various processes in industrial facilities. Calibration, testing, and maintenance of instruments ensure accurate measurement and control, reducing the risk of operational errors and emergencies.
Physical Activities/Procedures: Human factors play a significant role in safety-critical operations. Establishing and adhering to robust operational procedures, safety protocols, and training programs are essential for minimizing human error and promoting a safety-conscious culture among personnel.
Other Risk Prevention / Mitigations: Beyond mechanical equipment and instruments, safety critical elements may encompass various risk reduction tools, including process containment, ignition control, emergency shutdown systems, fire suppression systems, and environmental monitoring systems. Regular testing, inspection, and maintenance of these systems are crucial for swift and effective responses to emergencies.
Maintaining Safety Critical Equipment
Effective maintenance of safety-critical elements is often required by regulation. Regular maintenance activities, such as preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance, and corrective maintenance, help identify potential issues before they escalate into safety incidents or equipment failures.
1. Enhanced Safety: Proactive maintenance practices help identify and address potential safety hazards before they compromise personnel safety or environmental integrity.
2. Optimized Performance: Well-maintained safety-critical elements contribute to operational reliability, efficiency, and productivity, reducing downtime and enhancing overall performance.
3. Compliance Assurance: Adherence to maintenance best practices ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, mitigating legal and financial risks.
4. Cost Savings: Investing in proactive maintenance can result in cost savings by preventing costly equipment failures, emergency repairs, and unplanned downtime.
Putting it in Action
In the complex and dynamic environment of high-hazard industrial facilities, the identification, classification, and maintenance/ management of safety-critical elements is one of the most important activities to maintain safe operations. By prioritizing maintenance activities and adopting a proactive approach to risk management, organizations can safeguard their operations, protect their workforce, and uphold their commitment to safety and environmental stewardship.
Don’t be reckless! Contact RskLess to better understand the role of safety-critical equipment in ensuring a safer, more resilient future for your operations.